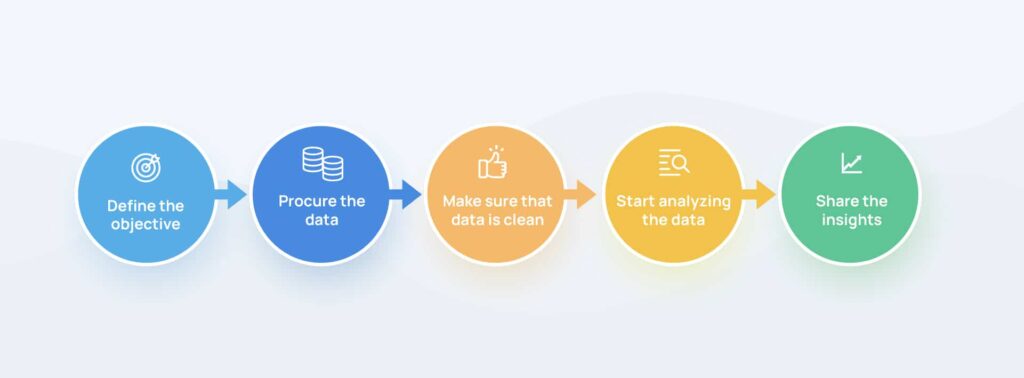
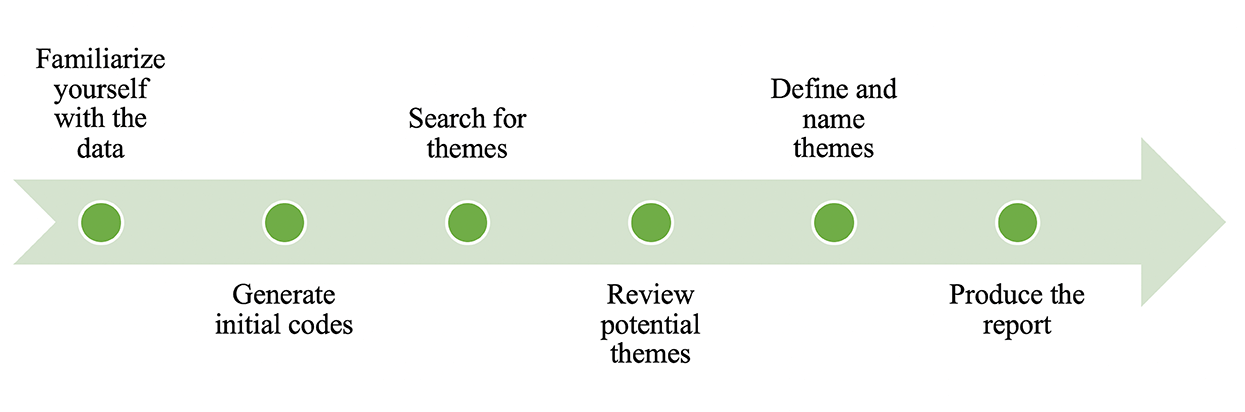
Data analysis is a process wherein data sets are examined to derive conclusions from the information they contain, and often with the help of specialized systems and software. It is the process of cleaning, combining and transforming data to gain meaning.
Types of Data Analysis
Descriptive Analysis:
Describes the basic features of data, including mean, median, mode, standard deviation.
Gives a high level overview of the dataset
Diagnostic Analysis:
Explores the root cause of a specific outcome, result or trend
Is frequently the result of drilling down into data to discover things are not as expected.
Predictive Analysis:
Uses past data to predict the trends and results that are likely to occur in future.
Methods such as statistical modeling and machine learning are typically employed.
Prescriptive Analysis:
Suggests courses of Action or decisions based on predictive analytics.
Often include the optimization techniques to find the optimal course of action.
Techniques and Tools in Data-Analyses
Statistical Software:
Statistical software packages — SPSS, SAS, and R for data analysis
Data Visualization Tools:
Visualization is done using tools like Tableau, Power BI, and libraries in Python such as Matplotlib and Seaborn to present data.
Machine Learning:
We can use algorithms such as linear regression, decision trees, and neural networks for predictive analysis and pattern recognition.
Data Mining:
Hidden patterns and insights can be discovered using various techniques such as clustering, association rule mining, and anomaly detection.
Uses for Data Analysis Data analysis can take place in a variety of areas such as:
Business — Making data-driven decision in marketing, operations and finance.
Healthcare: Discovering disease patterns, improving patient treatment, as well as working on new treatments.
Finance: Evaluating risk, predicting market trends, and maximizing investment strategies.
Government: From crafting policy decisions and assessing social services to enriching citizen engagement.
Science: Experiment data analysis, new theory generation, natural phenomenon(mathematics) understanding.
As technology proceeds to develop and information are increasingly more plentiful, data analysis will assume a far superior part than before in innovativeness and deciding across different businesses.
Interested in a particular kind of data analysis or real-world use you can think about?