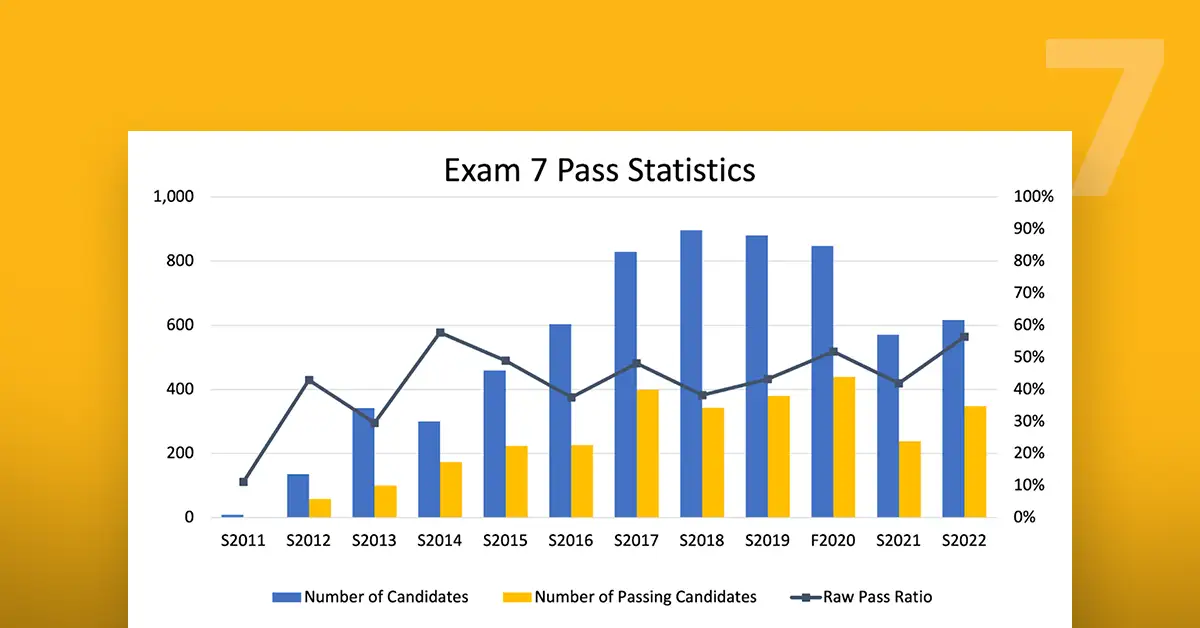
A pass rate is a quantifiable statistic denoting the number of people who achieved success in passing a delineated task, examination or course. It’s frequently used to measure the success of an educational program, training course, or certification exam.
Calculating Pass Rate:
Pass rate is the number of successful attempts divided by all attemps times 100.
Pass Rate = (Successful Attempts / Total Attempts) * 100
Importance of Pass Rate:
Program effectiveness: A pass rate that is high indicates that a program is successfully fulfilling its aims.
What role does it play under Quality Assurance: It maintains quality standards and ensures that the participants learn the skills and knowledge.
Resource Utilization: Pass rates can be used to guide resource utilization and program improvement.
Public Image: A good pass percentage adds to the credibility of institutions and organizations.
Factors Affecting Pass Rate:
Quality of the program The quality of instruction, curriculum and resources can have a significant impact on the pass rate.
Readiness of Students: What students bring to the classroom can affect their success.
Assessment methods—pass rates can be influenced by the fairness and reliability of assessment methods.
External Factors: Student performance can you be affected by external factors like economic conditions, social matters, global events etc.
Improving Pass Rate:
Ongoing Update: Curriculum and pedagogy should be regularly reviewed and updated.
Diversity of Assessment: Assess student learning with a range of assessment modalities.
Support for students: Provide services that support the student body, like tutoring and counseling
Welcome Data-Driven Decisions: Use passing data trends to drive decisions
Limitations of Pass Rate:
Pass rate is a great example of a good metric, but one that can only go so far.
May not represent the breadth of student learning: It is therefore limited in scope.