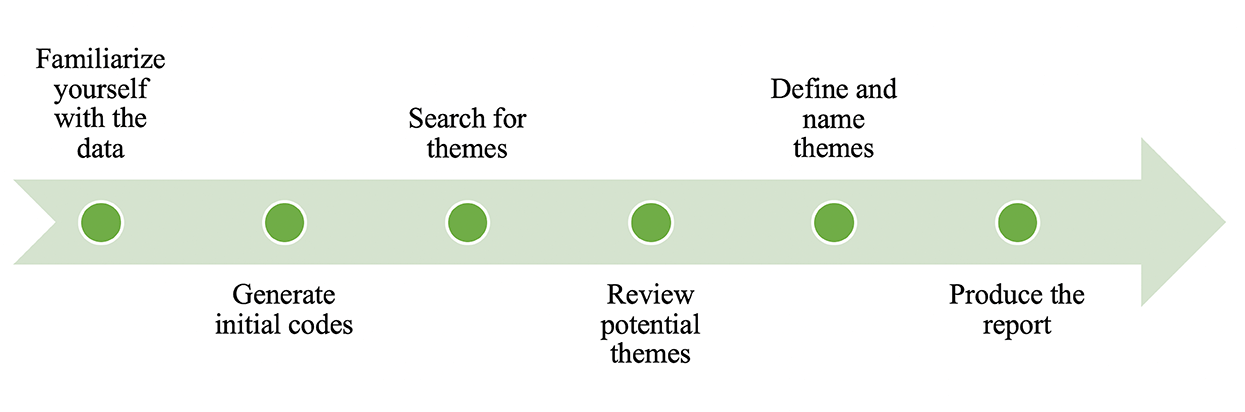
Thematic analysis [17] is a qualitative research method used for identifying, analyzing and interpreting patterns of meaning (themes) within qualitative data. It is a method for identifying, analyzing and reporting themes within data.
Zen Cook Use of thematic analysis – highlights the four key steps as identified by Braun and Clarke (2006) in conducting an inductive thematic analysis
Becoming acquainted: Read it or view it numerous times and bring your self into the data.
Generating initial codes : Find some initial codes or words that reflect what the content of the data is about.
Formulating a Coding Framework: Repeat the previous step as needed (for every transcripts) and combine your initial codes to create a more organized “coding framework.” This often indicates grouping codes that are similar to each other
Coding the Dataset: Code sections of the entire dataset according to the coding framework.
Identify Themes: Examine the coded data to discover common patterns and themes.
Writing-Up Themes: Conduct a deeper analysis to refine and develop the themes.
Analysing The Themes: Explain what the identified themes means or indicate its implication.
Types of Thematic Analysis
Inductive Thematic Analysis: a top-up method for generating themes based on the data.
Deductive Thematic Analysis: A top-down perspective in which thematic themes are drawn from pre-existing theory or research questions.
Exploratory thematic analysis: this is an inductive approach that provides a lot of flexibility but combines both deductive and inductive elements.
Examples of Thematic Analysis Themes As a flexible method, thematic analysis has many applications in different areas such as:
Social Sciences — The study of social phenomena, including attitudes, behaviors and cultural practices.
Humanities: Literature, history, and cultural studies.
health-sciences: It looks into patient experiences, healthcare practice and/or health policy.
Business and Management: Researching organizational culture, analyzing customer feedback, conducting marketing research.
Thematic analysis lets researchers learn not just about what meaning is derived around a structure in qualitative data — but it also helps them understand how any of the differing structures operate with the same fullness.